§The template engine
§A type safe template engine based on Scala
Play comes with a powerful Scala-based template engine, whose design was inspired by ASP.NET Razor. Specifically it is:
- compact, expressive, and fluid: it minimizes the number of characters and keystrokes required in a file, and enables a fast, fluid coding workflow. Unlike most template syntaxes, you do not need to interrupt your coding to explicitly denote server blocks within your HTML. The parser is smart enough to infer this from your code. This enables a really compact and expressive syntax which is clean, fast and fun to type.
- easy to learn: it allows you to quickly become productive, with a minimum of concepts. You use simple Scala constructs and all your existing HTML skills.
- not a new language: we consciously chose not to create a new language. Instead we wanted to enable Scala developers to use their existing Scala language skills, and deliver a template markup syntax that enables an awesome HTML construction workflow.
- editable in any text editor: it doesn’t require a specific tool and enables you to be productive in any plain old text editor.
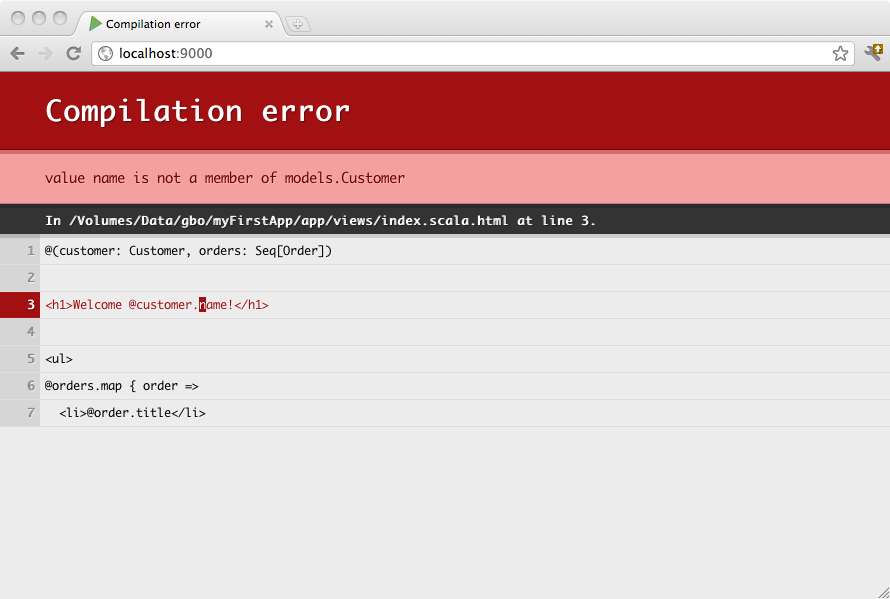
Templates are compiled, so you will see any errors in your browser:
§Overview
A Play Scala template is a simple text file that contains small blocks of Scala code. Templates can generate any text-based format, such as HTML, XML or CSV.
The template system has been designed to feel comfortable to those used to working with HTML, allowing front-end developers to easily work with the templates.
Templates are compiled as standard Scala functions, following a simple naming convention. If you create a views/Application/index.scala.html template file, it will generate a views.html.Application.index class that has an apply() method.
For example, here is a simple template:
@(customer: Customer, orders: List[Order])
<h1>Welcome @customer.name!</h1>
<ul>
@for(order <- orders) {
<li>@order.title</li>
}
</ul>You can then call this from any Scala code as you would normally call a method on a class:
val content = views.html.Application.index(c, o)§Syntax: the magic ‘@’ character
The Scala template uses @ as the single special character. Every time this character is encountered, it indicates the beginning of a dynamic statement. You are not required to explicitly close the code block - the end of the dynamic statement will be inferred from your code:
Hello @customer.name!
^^^^^^^^^^^^^
Dynamic codeBecause the template engine automatically detects the end of your code block by analysing your code, this syntax only supports simple statements. If you want to insert a multi-token statement, explicitly mark it using brackets:
Hello @(customer.firstName + customer.lastName)!
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
Dynamic CodeYou can also use curly brackets, to write a multi-statement block:
Hello @{val name = customer.firstName + customer.lastName; name}!
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
Dynamic CodeBecause @ is a special character, you’ll sometimes need to escape it. Do this by using @@:
My email is bob@@example.com§Template parameters
A template is like a function, so it needs parameters, which must be declared at the top of the template file:
@(customer: Customer, orders: List[Order])You can also use default values for parameters:
@(title: String = "Home")Or even several parameter groups:
@(title: String)(body: Html)§Iterating
You can use the for keyword, in a pretty standard way:
<ul>
@for(p <- products) {
<li>@p.name ($@p.price)</li>
}
</ul>Note: Make sure that
{is on the same line withforto indicate that the expression continues to next line.
§If-blocks
If-blocks are nothing special. Simply use Scala’s standard if statement:
@if(items.isEmpty) {
<h1>Nothing to display</h1>
} else {
<h1>@items.size items!</h1>
}§Declaring reusable blocks
You can create reusable code blocks:
@display(product: Product) = {
@product.name ($@product.price)
}
<ul>
@for(product <- products) {
@display(product)
}
</ul>Note that you can also declare reusable pure code blocks:
@title(text: String) = @{
text.split(' ').map(_.capitalize).mkString(" ")
}
<h1>@title("hello world")</h1>Note: Declaring code block this way in a template can be sometime useful but keep in mind that a template is not the best place to write complex logic. It is often better to externalize these kind of code in a Scala class (that you can store under the
views/package as well if you want).
By convention a reusable block defined with a name starting with implicit will be marked as implicit:
@implicitFieldConstructor = @{ MyFieldConstructor() }§Declaring reusable values
You can define scoped values using the defining helper:
@defining(user.firstName + " " + user.lastName) { fullName =>
<div>Hello @fullName</div>
}§Import statements
You can import whatever you want at the beginning of your template (or sub-template):
@(customer: Customer, orders: List[Order])
@import utils._
...To make an absolute resolution, use root prefix in the import statement.
@import _root_.company.product.core._If you have common imports, which you need in all templates, you can declare in build.sbt
templatesImport += "com.abc.backend._"§Comments
You can write server side block comments in templates using @* *@:
@*********************
* This is a comment *
*********************@You can put a comment on the first line to document your template into the Scala API doc:
@*************************************
* Home page. *
* *
* @param msg The message to display *
*************************************@
@(msg: String)
<h1>@msg</h1>§Escaping
By default, dynamic content parts are escaped according to the template type’s (e.g. HTML or XML) rules. If you want to output a raw content fragment, wrap it in the template content type.
For example to output raw HTML:
<p>
@Html(article.content)
</p>Next: Common use cases